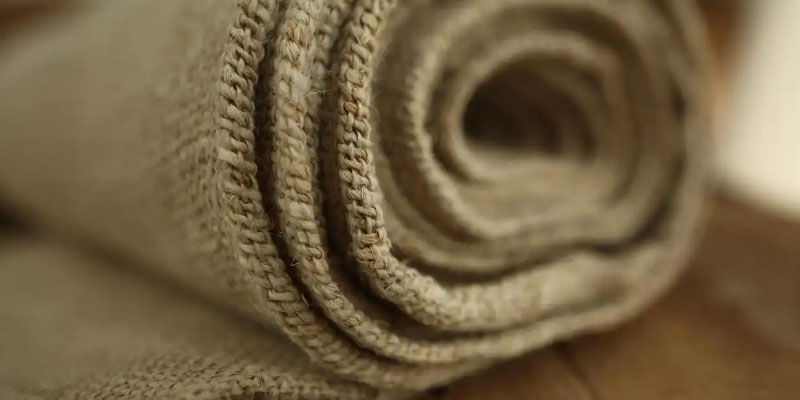
1:What is The Fiber Linen Fabric?
Fiber Linen Fabric is a textile made from the fibres of the flax plant. Linen fibres possess excellent moisture absorption, breathability and antibacterial properties, making them widely used in clothing, home textiles and other fields. Linen fabric has a soft texture and comfortable feel, giving a natural, eco-friendly impression.
2.The advantages of linen fabric
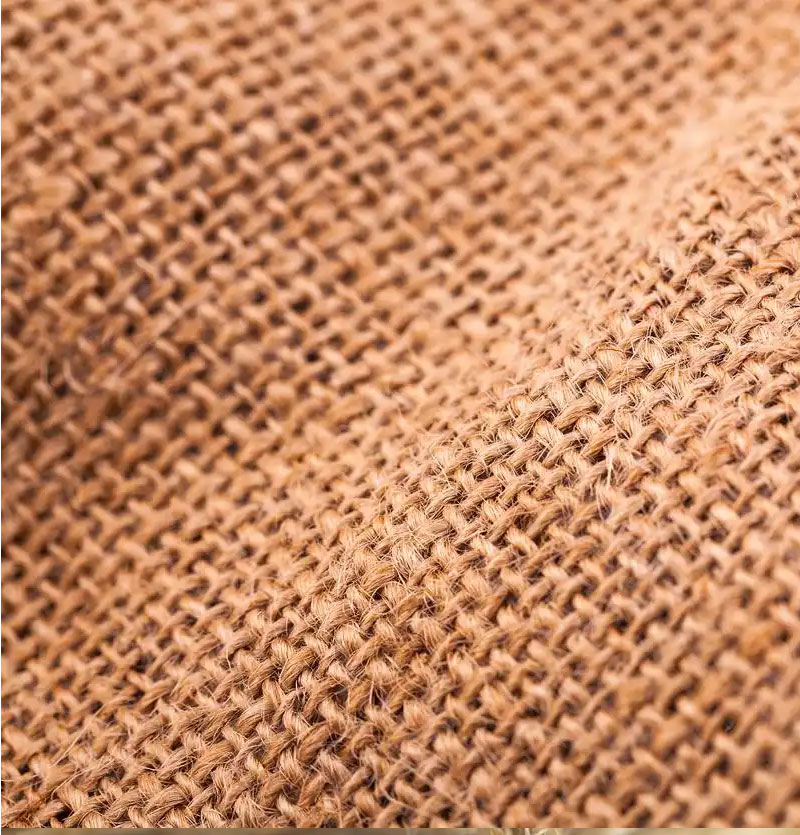

1. Moisture-wicking and breathable: Linen fabric absorbs moisture three times more effectively than cotton and offers twice the breathability, swiftly drawing away surface moisture to keep skin dry.
2. Antibacterial and odour-resistant: Linen fibres contain abundant natural antimicrobial substances that effectively inhibit bacterial growth and minimise odour formation.
3. UV Protection: Linen fabric provides excellent shielding against ultraviolet rays, effectively safeguarding skin from sun damage.
4. Eco-Friendly and Healthy: As a natural renewable resource, flax cultivation requires no chemical fertilisers or pesticides, making it exceptionally beneficial for both human health and the environment.
3.Disadvantages of linen fabric
1. Prone to creasing: Due to the relatively low rigidity of linen fibres, they are susceptible to creasing and require frequent ironing to maintain their appearance.
2. Prone to shrinkage: Linen fabrics tend to shrink during washing, necessitating careful control of water temperature and washing methods.
3. Poor abrasion resistance: Compared to other textiles, linen fabrics exhibit inferior wear resistance and are susceptible to abrasion.
4.Classification of linen fabric
—Flax: The Queen of Fibres
Flax, also known as the ‘Queen of Fibres,’ is primarily cultivated in France, Ireland, and Belgium, with France being its premier production region. Commonly, linen garments feature a thread count of 21 or higher, offering breathable lightness though prone to creasing. For bedding, thread counts of 12 and 14 are prevalent, with 14-count exhibiting superior performance—soft to the touch yet not overly thin. Flax fibres are longer than hemp but shorter than ramie, offering high strength and durability.
—Ramie: The Longest Fibre

Ramie fibres boast the longest single-fibre length among the three, suitable for both coarse yarns and high-count imitations of 120-count fabrics. However, due to its high strength and low elasticity, it can feel stiff and coarse in bedding, making ramie bedding uncommon.
—Linen-Cotton: Blends and Interweaves
Linen-cotton refers to fabrics blended or interwoven with linen and cotton, commonly found in ratios such as 70% cotton + 30% linen or 45% cotton + 55% linen. The higher the linen content, the drier and more breathable the fabric. A mere 10% linen content suffices to impart anti-static properties, though bedding with higher linen percentages commands a correspondingly higher price. Compared to blended fabrics, the interweaving process demands superior quality linen fibres. This technique preserves the inherent characteristics of linen more fully, resulting in enhanced comfort and a higher price point.

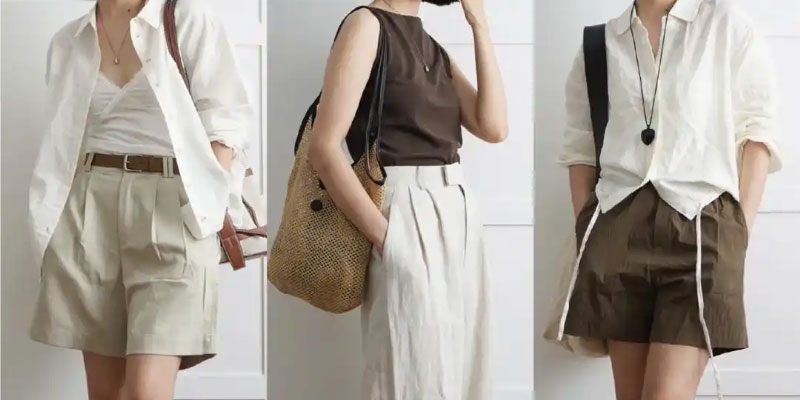
5.Usage of linen fabric
1. Automotive Industry: Linen composites used in door panel linings achieve 20% weight reduction
2. Architectural Decoration: Specially treated linen wallcoverings exhibit VOC adsorption capabilities
3. Medical Sector: Linen non-woven fabrics in disposable medical dressings pass ISO 10993 testing
6.Characteristics of Linen Fabrics
Natural linen fabrics possess inherent properties such as breathability, moisture-wicking, antibacterial and anti-mite qualities, and anti-static effects. However, the textured appearance, creasing, and natural knots inherent to linen weaves are unavoidable. Linen fabrics, with their distinctive advantages, remain an ideal choice for summer garments. Whilst certain drawbacks exist, the inherent benefits of linen can still be fully realised through proper washing and care methods.
Related posts